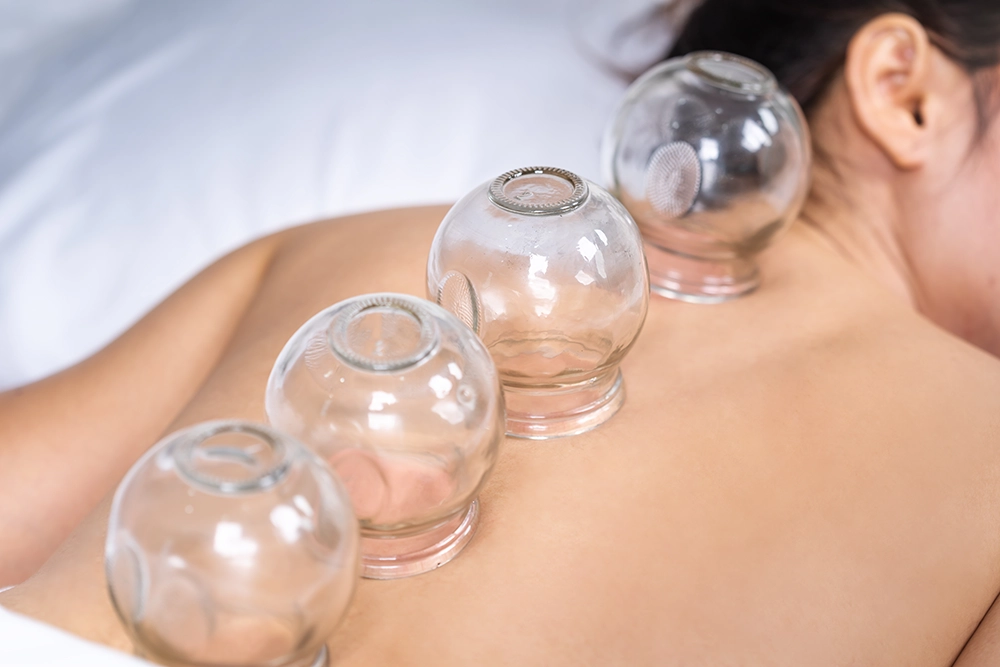

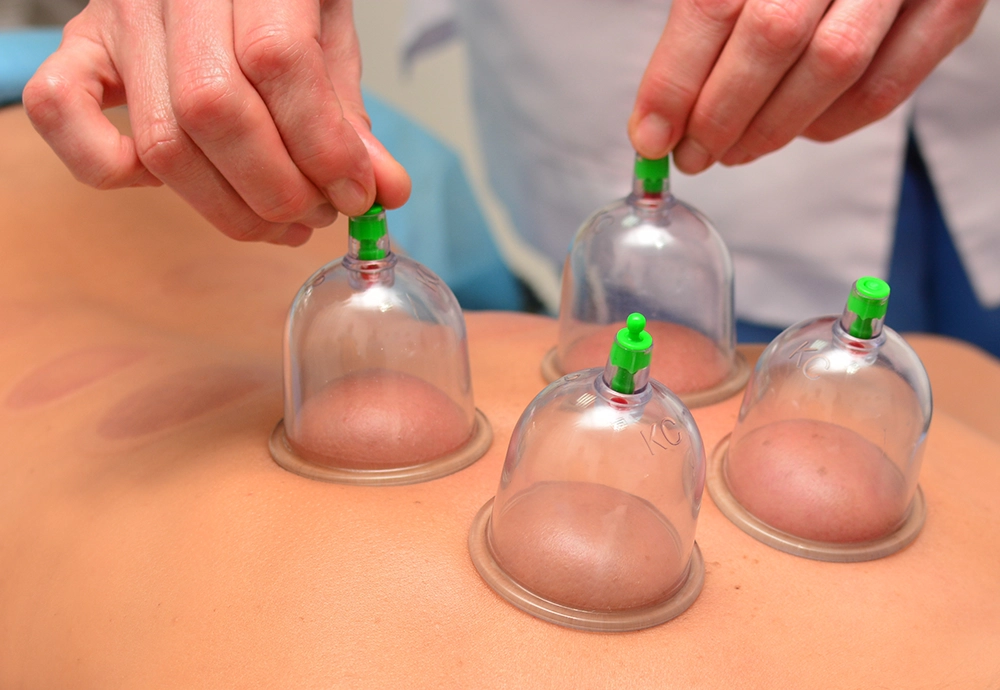
TCM cupping is a traditional healing method that applies negative pressure to the skin using cups, usually made of silicone, glass, or bamboo. This suction helps the body expel harmful elements like wind, cold, dampness, and heat by promoting the flow of blood and Qi (vital energy), which clears stagnation in the body meridians.
Cupping raises the tissue upward in contrast to massage, which applies pressure inward. It is thought that this distinction aids in enhancing lymphatic and blood circulation, eliminating toxins, and fostering deeper healing.
According to TCM theory, Cupping:
Additionally, the suction effect produces microtrauma, which sets off the body’s natural healing response.
Musculoskeletal problems like shoulder and neck tension are successfully relieved by cupping, pain in the lower back, joint and knee pain, sciatica.
Cupping is helpful during flu seasons or when recovering from minor illnesses because it helps prevent recurrent infections by boosting the body's defence mechanisms.
Those who suffer from sleeplessness or fatigue brought on by stress can benefit from cupping's calming effects on the nervous system.
Cupping works well for common ailments like arthritis, headaches, and body aches brought on by changing weather. It is especially helpful for those who have persistent sinus congestion or cold limbs.
By encouraging improved circulation and Qi flow to the stomach and spleen meridians, TCM cupping can control digestion. It is frequently used to treat conditions like constipation, bloating, and poor appetite.
Bloodletting cupping, sometimes referred to as wet cupping or Hijama cupping, goes one step further than traditional cupping by drawing blood and Qi to the surface by allowing a small amount of stagnant blood to leave the body.
Before applying the cup, a practitioner of bloodletting cupping uses a sterile lancet or needle to make tiny, superficial punctures. The suction then extracts a tiny quantity of blood, which is regarded as “toxic” or “stagnant” in TCM. Heat, stasis, and infections that are stuck in the bloodstream can all be removed with this technique.
Only qualified and licensed TCM physicians should perform bloodletting. It should not be used for:
Used to lower body temperature when there is a high fever, acne, or skin inflammation
It is thought that bloodletting at specific locations can help release tension or excess pressure
May be applied to certain points to treat blood stagnation or painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea)
Improves blood circulation and prevents disease by eliminating "stagnant" blood
Particularly useful for sharp or severe pain brought on by blood stasis
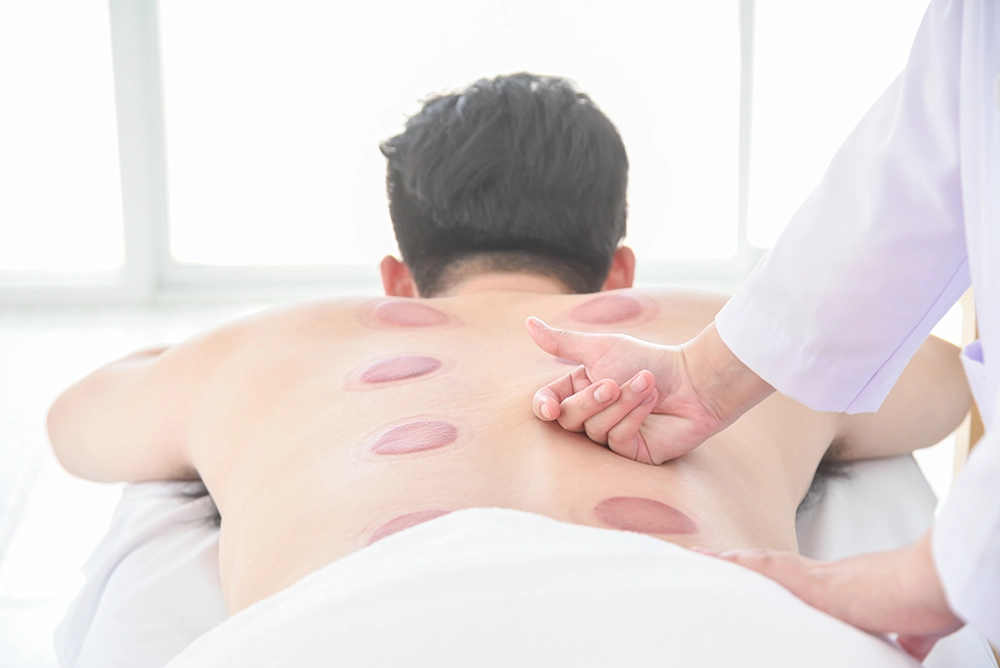
| Colour | TCM Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Pale or grayish | Cold or damp accumulation |
| Bright red | Excess heat or yin deficiency |
| Dark purple | Blood stasis or poor circulation |
| Blistering | Dampness or intense heat toxin |
These marks typically fade within a few days to two weeks, depending on the individual’s condition and metabolism.
To maximize benefits and avoid adverse reactions:
It is advisable to consult a TCM physician prior to any treatment.

At Liang Yi TCM, we provide Cupping / Blood Letting Cupping as part of our wellness therapy, and TCM treatments. If you would like to know more, feel free to contact us and we will be in touch soon.